Determining the Role of Maternally-Expressed Genes in Early Development with Maternal Crispants

Mater, a maternal effect gene required for early embryonic development in mice

Paternally expressed genes predominate in the placenta

KPNA7 is vital for the maintenance of proper nuclear morphology. a

Rapid generation of maternal mutants via oocyte transgenic expression of CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNAs in zebrafish
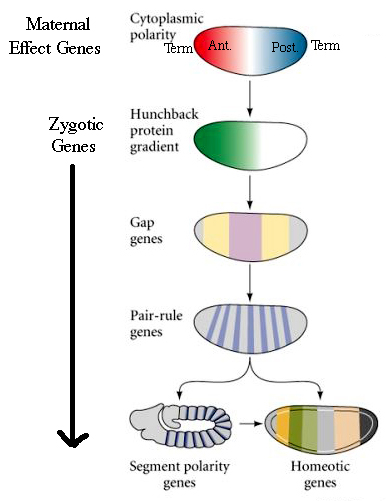
Developmental Biology 3230

Larvae lacking maternal rest show an atypical spatial preference at 6

PDF] Epigenetic mechanisms and the transgenerational effects of maternal care

Identification of Maternal-Effect Genes in Zebrafish using Maternal Crispants

Maternal Lineage - an overview

CRISPR/Cas9 technology: applications in oocytes and early embryos, Journal of Translational Medicine

Loss of Fgf-responsive Pea3 transcription factors results in ciliopathy-associated phenotypes during early zebrafish development
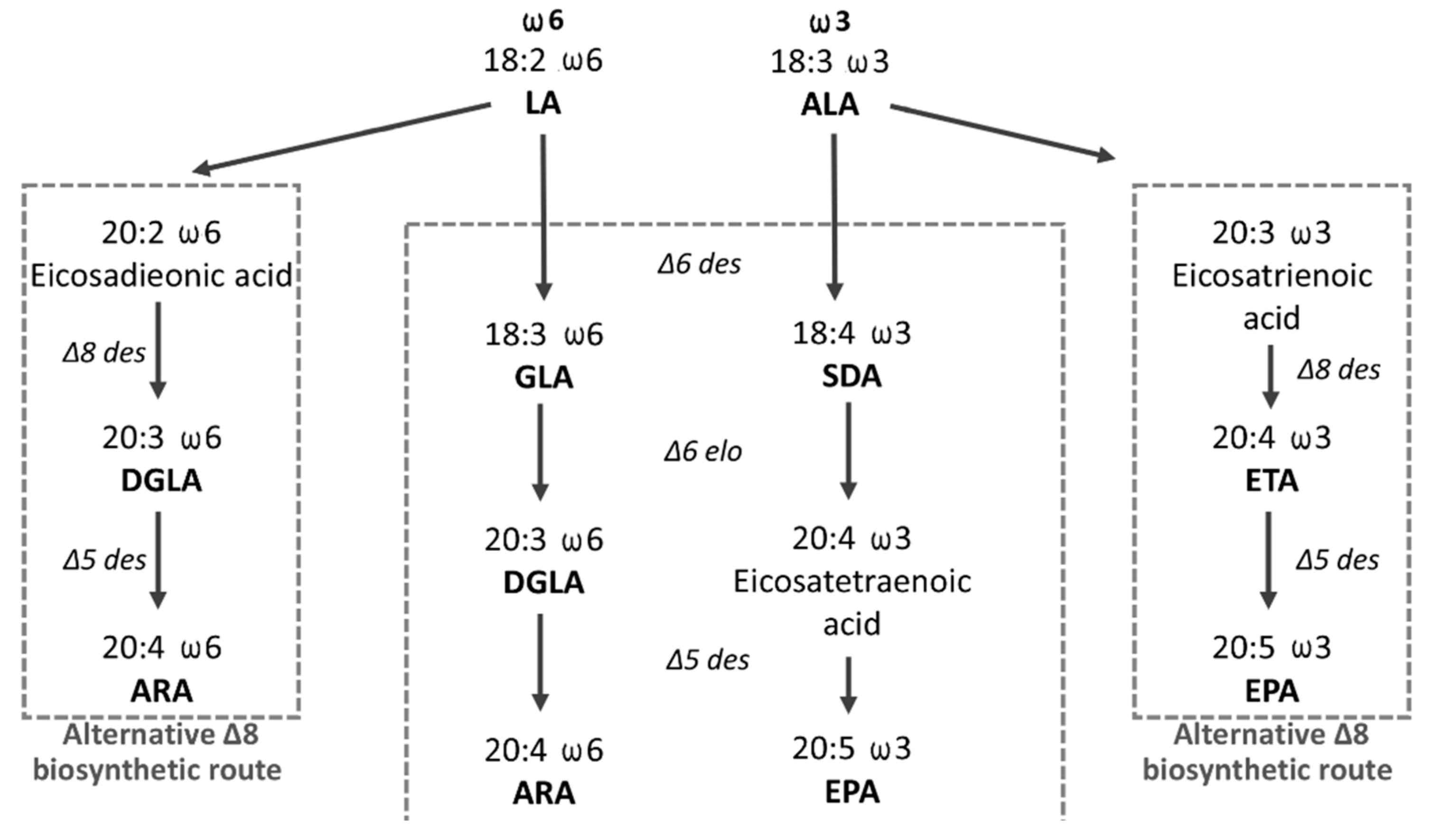
Genes, Free Full-Text

Early zebrafish development: it's in the maternal genes.
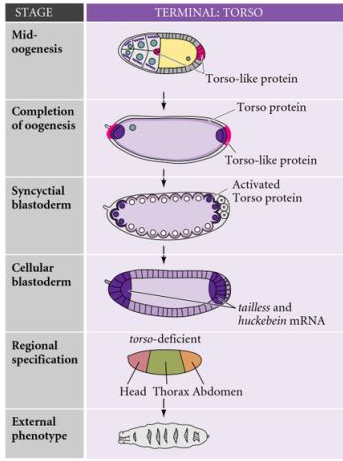
Developmental Biology 3230








