
Light microscopy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N (a, b) and PEN (c, d).
Download scientific diagram | Light microscopy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N (a, b) and PEN (c, d). Cells suspended in PBS and mixed with ammonium sulfate 0.02 M, pH 6.8 are shown in a and c, arrows from publication: The effect of cell surface components on adhesion ability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus | The aim of this study was to analyze the cell envelope components and surface properties of two phenotypes of Lactobacillus rhamnosus isolated from the human gastrointestinal tract. The ability of the bacteria to adhere to human intestinal cells and to aggregate with other | Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Adhesion and Exopolysaccharide | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Lactobacillus plantarum surface-displayed Eimeria tenella profilin
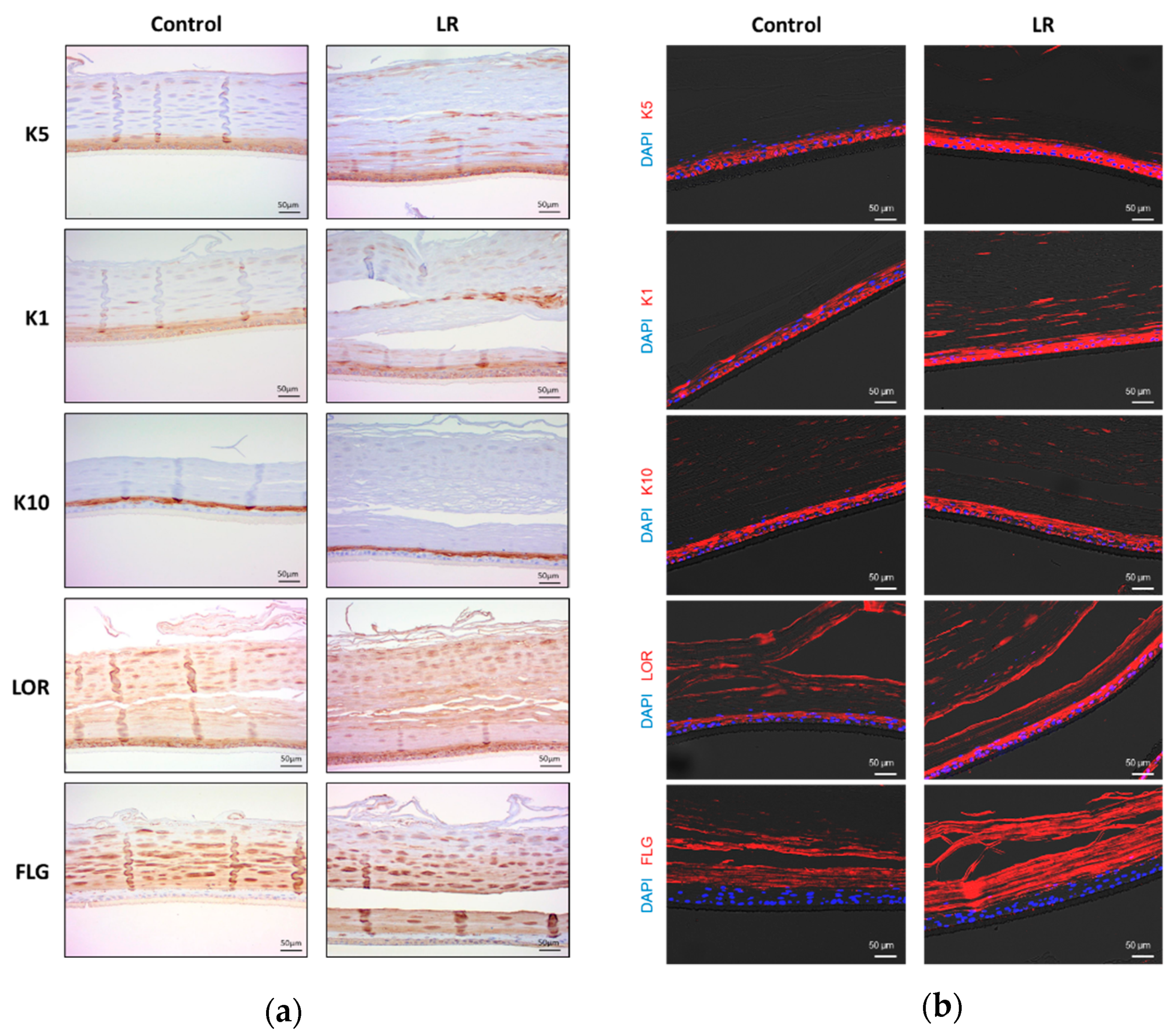
Animals, Free Full-Text
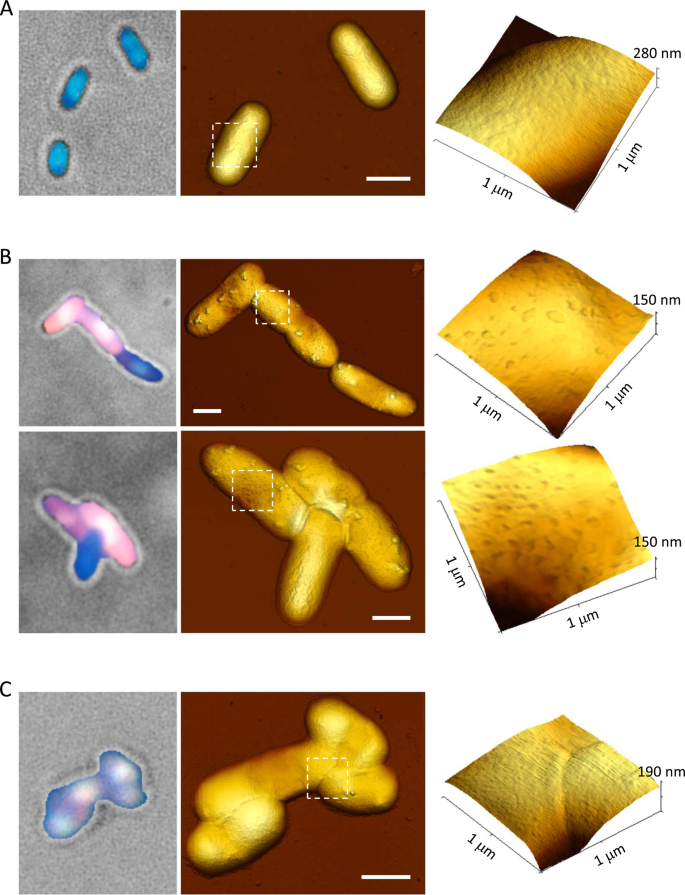
Functional characterization of the type I toxin Lpt from

Dose-Dependent Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus on Serum

Lactobacillus rhamnosus bacteria, SEM - Stock Image - C037/4523
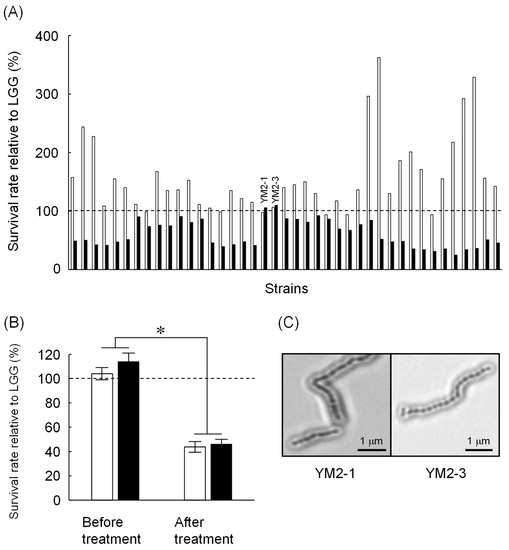
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Bifidobacterium breve and Lactobacillus rhamnosus treatment is as

Lactobacillus reuteri strains protect epithelial barrier integrity

Wnt5A Signaling Regulates Gut Bacterial Survival and T cell

Tetracycline-loaded zirconium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by

The potential probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-3690 strain

Flagellum staining of 16 strains of Lactobacillus ruminis using
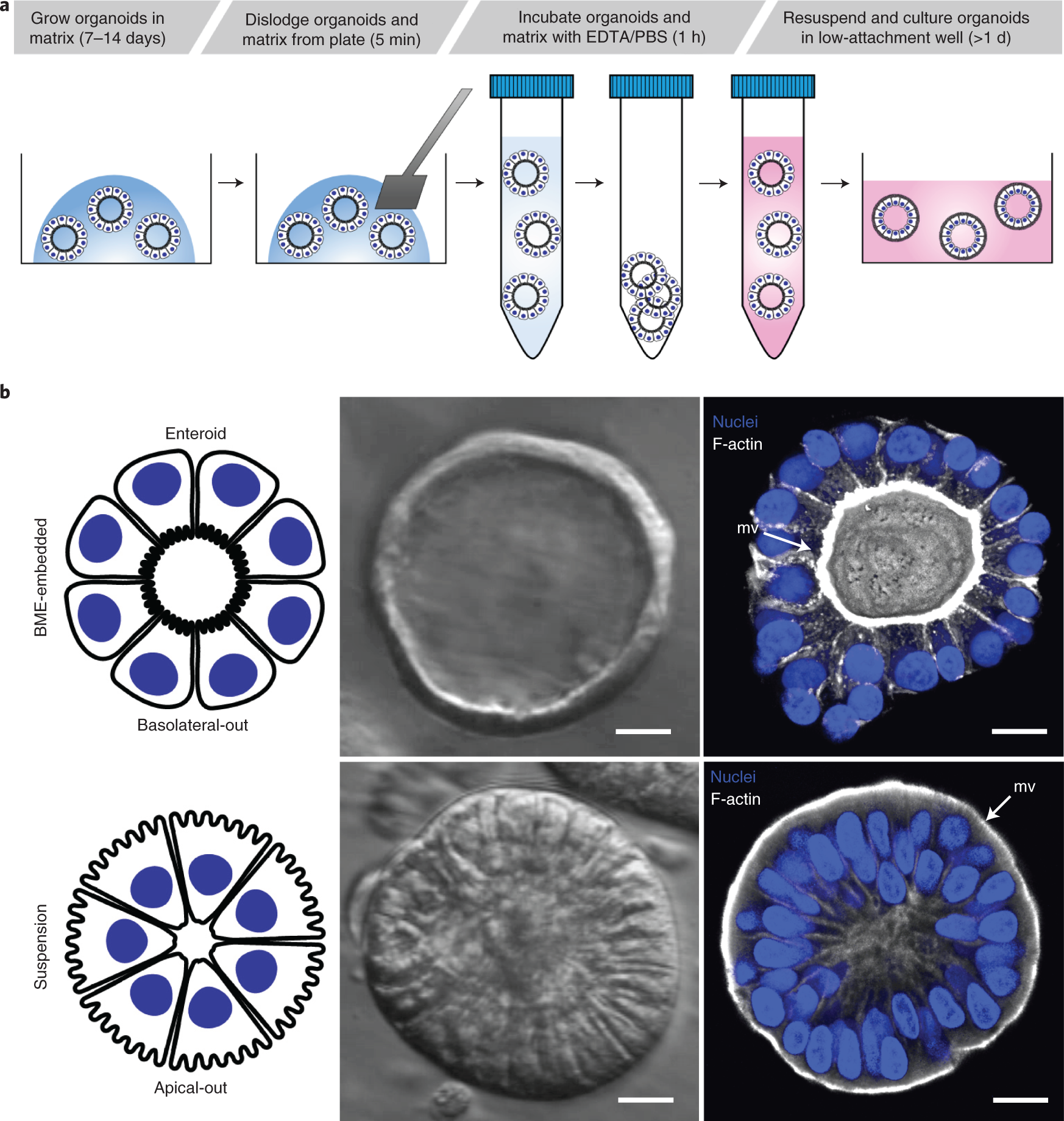
Controlling the polarity of human gastrointestinal organoids to

Bifidobacterium breve and Lactobacillus rhamnosus treatment is as

An early-life microbiota metabolite protects against obesity by








)